Initial concepts
So, what we can do with the Platform?
Register and login
First Steps - Creating your project
Profile
Permission System
Project Dashboard
Platform Glossary
Changing the Platform Language
2-Factor Authentication
Invalid authentication code
Artificial Intelligence
Human Attendance
Weni Chats: Introduction to the Chats module
Weni Chats: Human Service Dashboard
Weni Chats: Attendance distribution rule
Weni Chats: Using active triggering of flows
Using groups to organize human attendance
Studio
Contacts and Messages
Groups
Messages
Triggers and Campaigns
Adding a trigger
Triggers Types
Tell a flow to ignore triggers and keywords
Campaign introduction
How to create a Campaign
Editing events
Creating contact from an external Webhook
Contact history
How to Download and Extract Archived Data
Integrations
Settings
How to connect and talk to the bot through the settings
Adding a Facebook Channel
Adding a Viber channel
How to Create an SMS Channel - For Developers (RapidPro)
Web Chat Channel
General API concepts and Integrations
How to create a channel on twitter
How to create a channel on Instagram
How to create an SMS channel
Adding ticket creation fields in Zendesk
Adding Discord as a channel
Creating a Slack Channel
Adding a Viber channel (RapidPro)
Creating a Microsoft Teams channel
Weni Integrations
How to Use the Applications Module
How to Create a Web Channel
Adding a Telegram channel
How to create a channel with WhatsApp Demo
Whatsapp: Weni Express Integration
Whatsapp: How to create Template Messages
WhatsApp Template Messages: Impediments and Configurations
Supported Media Sending - WhatsApp Cloud
Zendesk - Human Support
Ticketer: Ticketer on Rapid Pro
Whatsapp Business API
Active message dispatch on WhatsApp
Whatsapp business API pricing
How to Verify My Business
Whatsapp Bussiness API: WhatsApp message triggering limitation
Regaining Access to Business Manager
Webhook Configuration: Message Delivery Status
The Basics of Integrations
Native ChatGPT Integration
Native Integration - VTEX
General settings
General Project Settings
Weni Chats: Setting Up Human Attendance
Weni Chats: Human Service Management
Flows
Expressions and Variables Introduction
Variables Glossary
Expressions Glossary
Flows Creation
Flows introduction
Flow editor and tools
Action cards
Zero Shot Learning
Decision cards
Adding Media to the message
Call Webhook: Making requests to external services
Import and export flows
Using expressions to capture the user's location
Viewing reports on the platform
Route markers
WhatsApp Message Card
UX Writing
Concepts
Good Practices for Chatbots Based on UX Writing
Hierarchy of information
Usability Heuristics for Chatbots
UX Text Standards
Weni CLI
- All Categories
- UX Writing
- Usability Heuristics for Chatbots
Usability Heuristics for Chatbots
Updated
by Mallu
The 10 usability heuristics were created by Jakob Nielsen, a computer scientist, to assess interface usability. However, they can also be applied to chatbot usability, as we will see below.
The examples below were taken from the video "Usability Heuristics for Bots."
- System Status Visibility: The user should know what is happening.
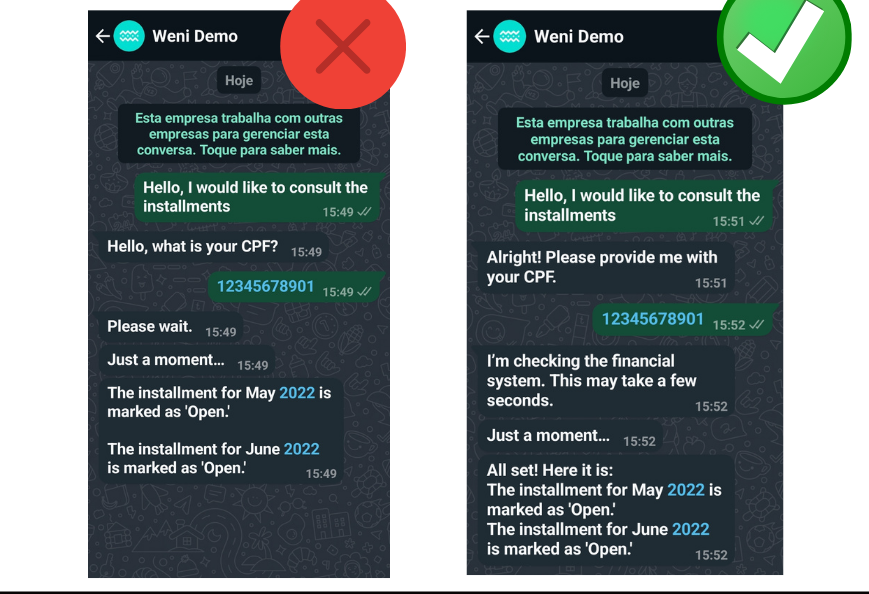
- Match Between System and Real World: The system should speak the user’s language, instead of using
technical terms that only make sense to developers.
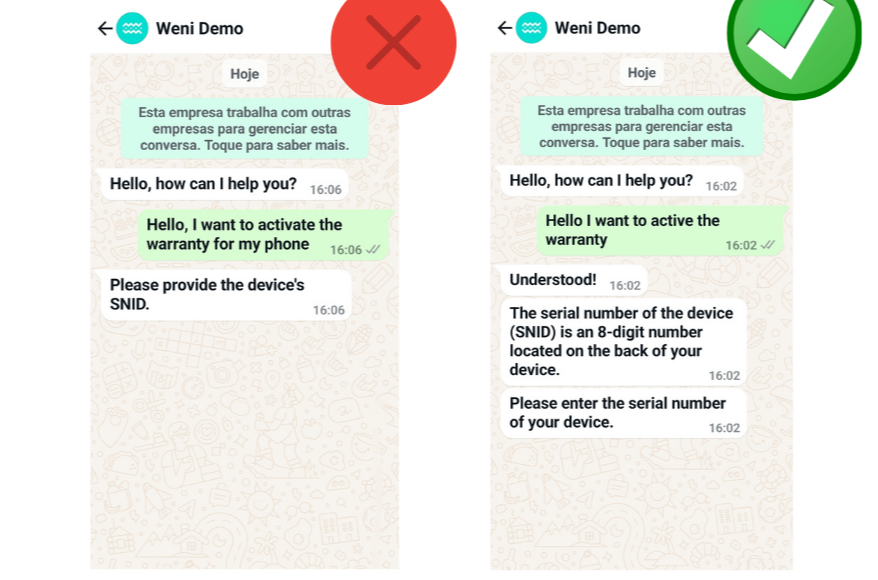
- User Freedom and Control: Users should have the freedom to go back, skip, or advance at any stage of the system.
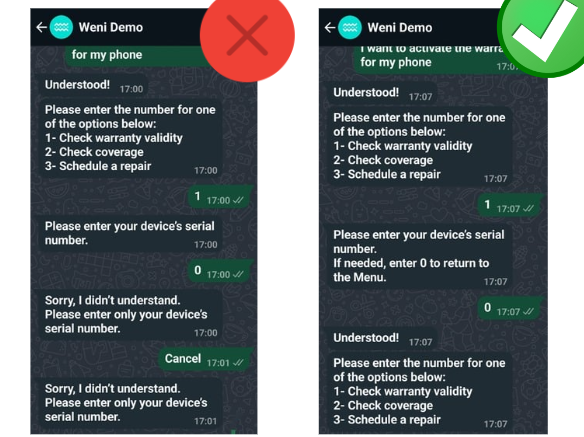
- Consistency and Standards: Users shouldn’t have to wonder if different words, situations, or actions mean the same thing. Use standardized language.
- Error Prevention: "Even better than a good error message is a careful design that prevents errors from happening."
- Recognition Rather Than Recall: Minimize the user’s memory load by making objects, actions, and options visible. The user shouldn’t have to remember information from one part of the dialogue to another.
- Flexibility and Efficiency of Use: The system should be fast for experienced users and flexible for beginners. Additionally, it should allow frequent tasks to be automated.
- Aesthetic and Minimalist Design: Dialogues shouldn’t contain irrelevant or rarely needed information. Each extra unit of information competes with relevant information and decreases its relative visibility. Write only what’s necessary.
- Help Users Recognize and Recover From Errors: Error messages should be expressed in simple language (without codes), clearly indicate the problem, and constructively suggest a solution.
- Help and Documentation: Even if the system can be used without documentation, it may be necessary to provide help and documentation. Make it available as an option or intent.
